In order to prevent another pandemic so soon after the last one, US authorities need to stop this new malaria outbreak in its tracks.
The female Anopheles mosquito plays host to the disease’s parasite. CC BY-SA 2.0
Over the past two months, seven cases of locally acquired malaria have been identified in the US. These cases, six of which appeared in Florida and one in Texas, have drawn significant attention as the first time in 20 years the disease has been transmitted domestically. At present, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported that all five patients have received medical treatment and are recovering positively, and that the risk of malaria reappearing in a more widespread epidemic across the U.S. is extremely low. That being said, this is a good reminder for those in charge of American public health infrastructure to reflect on how best to shore up national defenses, especially in the wake of the recent Covid-19 pandemic.
Malaria is caused by parasites, which commonly infect Anopheles mosquitoes, and who in turn transfer the disease to humans when they inject their proboscises into our bloodstreams. There are several species of the malaria parasite, collectively known as Plasmodium, some of which cause more serious cases than others, but all of which require tropical climates to thrive. Regardless of the species, malaria is still extremely serious and symptoms such as high fevers, chills, and nausea begin to manifest in a few weeks. Most worryingly is that malaria, if left untreated, is fatal. As of 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) believed that a grand total of 247 million cases of malaria occurred around the world, of which 619,000 were fatal. The majority of these deaths were children in various countries in Africa, where malaria is a constant present threat and contributes to a vicious cycle of social and economic poverty, taking a massive toll on countries in already precarious situations.
Malaria awareness in the US during the 1950s. Library of Congress. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
At the beginning of the 20th century, malaria was considered an extremely serious issue in the US; the CDC was actually founded in 1946 to eliminate the disease. Over the next six years, various public health measures such as insecticide use and window screens were implemented to reduce the 15,000 cases reported in 1947, and in 1951, the CDC finally announced that malaria was in the US no longer. This remained the case for decades, until an incident in 2003 when eight locally acquired cases in Palm Beach, Florida were identified. Fortunately, the outbreak was quickly quashed thanks to an immediate response campaign that completely rid the area of mosquitoes to prevent transmission. Since then, malaria has remained fairly absent from the American healthcare landscape.
It is important to note, however, that malaria has never been completely extinct in the US; prior to the recent COVID-19 pandemic, roughly 2,000 cases of the disease were identified and reported annually in patients who had traveled to countries with high incidences of malaria in Southeast Asia and Africa. Additionally, once infected individuals return to the US, local mosquitos who feed on them can pick up the parasite and spread it further. Every so often, this may result in a small reintroduction of the disease and potentially even some limited transmission, but there has never been any worry of it resulting in a much widespread epidemic.
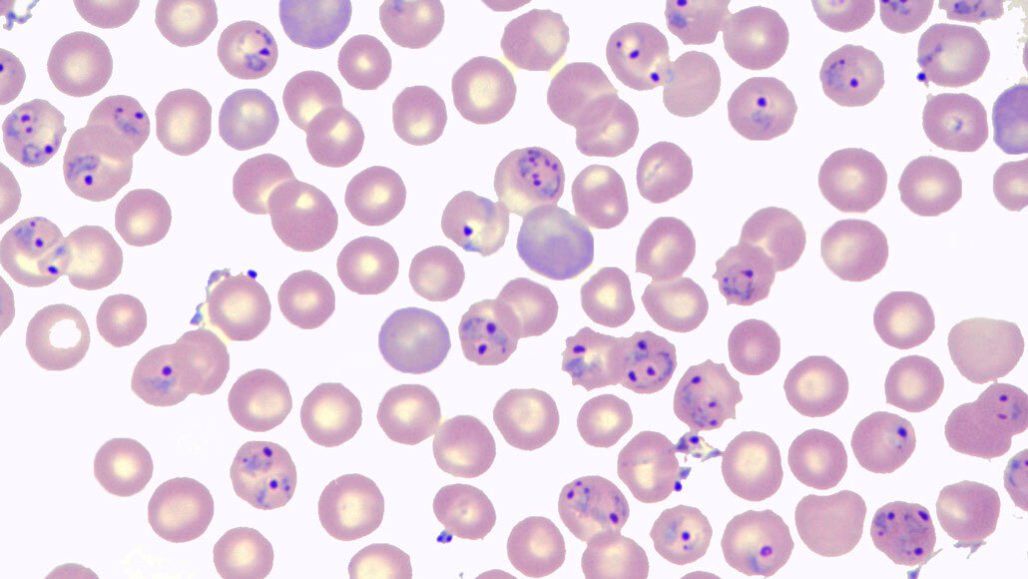
The malaria parasite pictured under a microscope. Joseph Takahashi Lab. CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
The reason these recent cases received so much attention were that all five were acquired locally within the US, which likely indicates that the parasitic mosquito population has made a resurgence as well. Thankfully, the species of parasite identified to have caused this small outbreak is known to transmit one of the milder forms of the disease, but that in no way detracts from the gravity of the situation. Matters of public health have become much more salient in regular discourse since the COVID-19 pandemic, and with it, some extreme opinions about containing and treating transmissible diseases. While America’s healthcare infrastructure continues to operate in largely the same way as it did during the 2003 outbreak, experts have agreed that public cooperation is now more important than ever if this re-appearance is to be nipped in the bud.
The RTS,S malaria vaccine. TheScientist. CC BY-SA 2.0
One particular area in which this agreement would go a long way, is that surrounding the efficacy of vaccines. In October of 2021, the WHO officially recommended the use of the RTS,S malaria vaccine developed by GlaxoSmithKline to prevent transmission in regions with high incidences of the disease. In addition to being logistically simple to store and administer, trials proved that the vaccine was beneficial to 90% of those treated, a staggering figure in the world of pharmaceutical development. Introducing the vaccine to the U.S. seems like an obvious step to take in the wake of these recent malaria cases, especially given the low price of a single dose at $9.30.
Vaccines have been a hotspot of controversy over the past few years, with many people denouncing both their safety and efficacy as a preventative treatment. Government authorities and healthcare professionals and academics around the world continue to release studies and evidence to show that vaccines are essential to build up individual and population-wide resistance to a variety of diseases, but large groups of the public still remain unconvinced. Among the many lessons and important takeaways from the COVID-19 pandemic, the importance of vaccinations is among the most important, especially in the face of a potential re-emergence of a disease as deadly as malaria.
Tanaya Vohra
Tanaya is an undergraduate student pursuing a major in Public Health at the University of Chicago. She's lived in Asia, Europe and North America and wants to share her love of travel and exploring new cultures through her writing.